"What to do? " - men and women wonder when they have hip pain. One of the most common causes of this symptom is osteoarthritis. In the article we will tell you why the hip joint hurts in men or women when walking and at rest, where the pain goes, what other pathologies it occurs and how to treat it. treat.
Hip joint degeneration (coxarthrosis)- degenerative-dystrophic disease. It usually appears in people after age 40, often as a result of trauma, but often begins with no apparent cause.
The disease is characterized by a slow and gradual progression. In the early stages, conservative treatment methods (medications, physical therapy) are often used. However, at a later stage, to restore the normal function of the joint, in certain cases surgery is required to replace the joint.
Many people suffer from coxarthrosis: this fact is due to the fact that the load on the hip joint is often large. In women, this condition occurs more often.
Factors that may increase the risk of developing this condition include prolonged and frequent heavy loading on the hip joint. Coxarthrosis often occurs in seemingly opposite groups of people: professional sports players and obese people. Other risk factors include diseases that affect blood circulation, metabolism and hormonal balance, and diseases of the musculoskeletal system (eg, feet, spine). Coxarthrosis is also more common in old age.
Mechanism of development of hip osteoarthritis
Anatomically, the hip joint consists of two bones:
- pelvis, with acetabulum;
- femur, with head. Doctors simply call the thigh bone the femur.
These two parts of the bone are connected together to form a joint. When a person moves his legs, the joint surfaces of the two parts in question rub against each other.
To avoid damage during this process, they are covered with elastic cartilage and synovial fluid is secreted there, which plays the role of lubrication. This happens in a healthy person. The hip joint essentially works like a hinge.
When a person suffers from coxarthrosis, the joint fluid becomes thicker and the cartilage becomes less elastic, cracks appear on it. As a result, the surfaces of the pelvis and femur are less protected during friction and are more susceptible to wear and damage. As a result, over time, they begin to change shape.
Symptoms of hip osteoarthritis
Among the main signs of this condition is pain. They are localized in the joint area, as well as in the groin, above the thighs.
The following symptoms are also typical:
- movement restrictions;
- when a person tries to move his leg to the right (if we are talking about right coxarthrosis) or to the left (when the left joint is affected), then he does not succeed completely;
- The gait becomes different from the gait usually seen in healthy people, the patient limps;
- decreased leg muscle mass;
- The affected leg becomes shorter.
Early stage of hip osteoarthritis
In the early stages of the development of the disease, pain sometimes occurs periodically, mainly after physical exertion. For example, after a person runs or walks a long distance. The feeling is concentrated in the hip joint, sometimes in the upper leg or even in the knee. When a person rests, the pain usually subsides. Walking is still normal at this stage. People can move their legs freely and their muscles are stable.
X-rays show that the joint space is narrowed, but not much. Where the edges of the acetabulum are present, bone spurs can be identified. At this stage, the head and neck of the femur do not change.
Evolution
In the next stage, the patient suffers more pain, occurring both during physical activity and at rest. They are strong, they go to the thighs, to the groin. After trying to run, a person may limp, just like after walking. Moving your legs sideways becomes more difficult and your range of motion is limited.
X-rays show strong and narrowing of the joint space. The images show displacement and deformity of the femoral head. Bone growth is visible in the acetabular area.
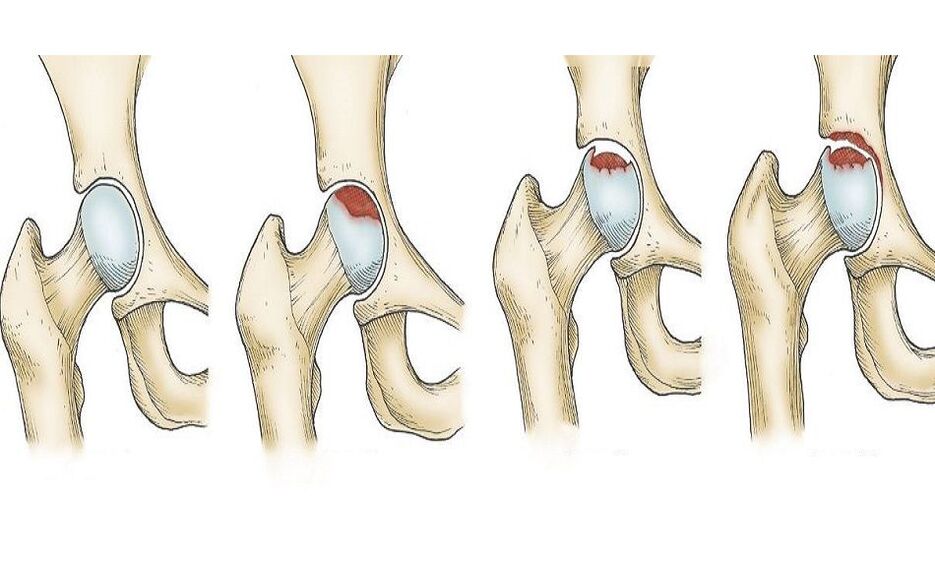
Late stage of hip osteoarthritis
Here the person had to endure severe pain continuously. They can occur not only during the day while resting, but also at night. The patient had difficulty walking, so he had to buy a cane. Moving your legs becomes even more difficult than before. At this stage, muscle atrophy in the legs and buttocks often occurs, causing the affected leg to become shorter. To walk more easily, a person leans to one side, and this further increases the load on large joints.
X-rays at this stage can show that the joint space is very narrow, the head of the femur is enlarged and there are many bones growing.
Diagnosis of hip osteoarthritis
It is carried out through a comprehensive examination, including:
- the doctor asks the patient;
- examination by a doctor;
- Ancillary studies, of course, the main study is X-rays.
On x-rays, you can sometimes detect the cause of osteoarthritis - for example, you can see signs of previous injury, dysplasia and other conditions.
CT scans (CT and MRI) also help with diagnosis. Using the first, you can study changes in bones, and with the second, you can study what happens to soft tissues.
What can hip osteoarthritis be confused with?
We wrote above that pain from coxarthrosis can occur not only in the hip joint, but also in the knee and throughout the entire upper leg.
This means that if such symptoms occur, the doctor must first rule out the following pathologies:
- osteoarthritis (because it also causes pain in the upper part of the leg);
- osteoarthritis of the knee joint (manifested as knee pain).
Osteoarthritis pain syndrome is different from hip osteoarthritis pain syndrome. With osteoarthritis, the pain is pronounced and is often provoked by something: for example, a person turning sharply or lifting a heavy object. In this case, the pain often spreads from the buttocks down the back of the leg.
With osteoarthritis, even when the pain is severe, a person can still move the leg left or right. But with coxarthrosis - not always.
When knee osteoarthritis occurs, pathological changes are detected on X-rays of the knee joint.
It should be remembered that a person can have many diseases at the same time. For example, osteoarthritis in both the knee and hip joints. Or osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis in some joints.
It is important to differentiate hip osteoarthritis from trochanteritis. The latter is inflammation of part of the femur, in Latin it is called Trochanter Major (trochanter Major) - larger trochanter. Trochitis occurs quickly, compared to osteoarthritis, the pain is stronger and the patient can move their legs freely.
In some cases, with the pain that makes one suspect hip osteoarthritis, some other condition is present (for example, ankylosing spondylitis, called ankylosing spondylitis, etc. ). . With them, as a rule, pain occurs at night, disappears during the day, and can even be relieved by physical activity.
Treatment of coxarthrosis
If you have joint pain, you should see an orthopedic surgeon.
Treatment includes conservative therapy (medication, physical therapy) and surgery.
Conservation therapy
Conservative treatment is prescribed in the early stages.
This includes:
- regular pain relievers that a person takes in pill or injection form (injection), ointment;
- hormones injected into joints;
- substances that restore the structure of cartilage (they are also taken orally and injected into the joint);
- Other medications are prescribed by the doctor depending on the patient's condition. These include drugs that relax muscles, dilate blood vessels, etc. v.
All medications must be taken strictly as prescribed by your doctor. This is especially true of common painkillers: with prolonged use, they can have a negative effect on the stomach and cause serious complications, including bleeding. Therefore, the duration of courses should be determined only by the doctor.
Physical therapy is also used in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis.
Many people benefit from laser and ultrasound treatment (this is called laser therapy and ultrasound therapy, respectively).
Magnetic therapy, touch therapy, light therapy and several other methods are used.
Therapy uses physical therapy (physical therapy) and massage.
It is worth saying a few words about diet. It does not directly treat hip osteoarthritis. However, when a person weighs less, the load on the joints is reduced, making the disease more susceptible.
Surgery to treat hip osteoarthritis
When the disease has reached a severe stage, the method that really "works" is surgery, when the diseased joint is replaced with an artificial joint. It's called endoscopy.
Different parts of the joint may change. For example, only the head of the femur. This is a unipolar prosthesis. When both the femoral head and the acetabulum are replaced, such a prosthesis is called a bipolar.
Endoscopic replacement is performed under general anesthesia. The first person is thoroughly examined. After surgery, treatment with antibiotics and anticoagulants is prescribed. The stitches are removed between the tenth and twelfth days, after which the person is transferred under the supervision of a doctor to a clinic or medical center, which provides outpatient care.
After surgery, the person is prescribed a series of rehabilitation measures.
In 95% of cases, after surgery, a person can walk, work, and some even play sports. An artificial joint "works" for fifteen to twenty years, after which a new surgery may be required.
Shock wave therapy is one of the effective treatment methods for chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, based on the impact of sound waves, giving quick results. After a course of shock wave treatment, you caneffective long-term therapy is possible.





































